|
|
 |
| |
back to top | |||
|
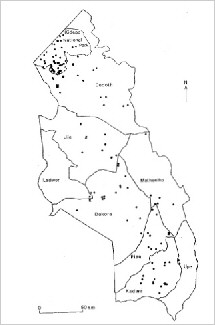
Population. Estimated less than 100. Small numbers are thought to be found in the north east sector of the country in Kidepo National Park (1,400 km2). Principal Threats. Poaching and loss of habitat. |
|
|
||
|
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
||||
|
Background: The colonial boundaries created by Britain to delimit Uganda grouped together a wide range of ethnic groups with different political systems and cultures. These differences prevented the establishment of a working political community after independence was achieved in 1962. The dictatorial regime of Idi AMIN (1971-79) was responsible for the deaths of some 300,000 opponents; guerrilla war and human rights abuses under Milton OBOTE (1980-85) claimed at least another 100,000 lives. The rule of Yoweri MUSEVENI since 1986 has brought relative stability and economic growth to Uganda. During the 1990s, the government promulgated non-party presidential and legislative elections. |
||||
| back to top | |
|
Area: total: 236’040
sq km; land: 199’710 sq km; water: 36’330 sq km
Climate: tropical; generally rainy with two dry seasons (December to February, June to August); semiarid in northeast Terrain: mostly plateau with rim of mountains Natural resources: copper, cobalt, limestone, salt Land use: arable land: 21.57%; permanent crops: 8.92%; other: 69.51% (2005) Irrigated land: 90 sq km (2003) Natural hazards: NA Environment-current issues: draining
of wetlands for agricultural use; deforestation; overgrazing; soil erosion;
poaching is widespread Environment-international agreements:
party to: Biodiversity, Climate
Change, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea,
Marine Life Conservation, Nuclear Test Ban, Ozone Layer Protection |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| back to top | ||
|
|
|
Population: 28,195,754; note: estimates for this country
explicitly take into account the effects of excess mortality due to AIDS; this
can result in lower life expectancy, higher infant mortality and death rates,
lower population and growth rates, and changes in the distribution of
population by age and sex than would otherwise be expected (July 2006 est.)
Age structure: 0-14 years: 50% (male 7,091,763/female 6,996,385); 15-64 years: 47.8% (male 6,762,071/female 6,727,230);65 years and over: 2.2% (male 266,931/female 351,374) (2006 est.) Female: 53.69 years (2006 est.) Median
age: total: 15 years; male: 14.9 years; female:
15.1 years (2006 est.) |
|
Population growth rate: 3.37% (2006 est.) Infant mortality rate: total: 66.15 deaths/1,000 live births; male: 69.51 deaths/1,000 live births ; female: 62.69 deaths/1,000 live births (2006 est.) Life expectancy at birth: total population: 52.67 years; male: 51.68 years; female: 53.69 years (2006 est.) Total fertility rate: 6.71 children born/woman (2006 est.) HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate: 4.1% (2003 est.) HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS: 530,000 (2001 est.) HIV/AIDS - deaths: 78,000 (2003 est.) |
||
|
Ethnic groups: Baganda 17%, Karamojong 12%, Basogo 8%, Iteso 8%, Langi 6%, Rwanda 6%, Bagisu 5%, Acholi 4%, Lugbara 4%, Bunyoro 3%, Batobo 3%, non-African (European, Asian, Arab) 1%, other 23% Religions: Roman Catholic 33%, Protestant 33%, Muslim 16%, indigenous beliefs 18% Languages: English (official national language, taught in grade schools, used in courts of law and by most newspapers and some radio broadcasts), Ganda or Luganda (most widely used of the Niger-Congo languages, preferred for native language publications and may be taught in school), other Niger-Congo languages, Nilo-Saharan languages, Swahili, Arabic Literacy: definition: age 15 and over can read and write; total population: 69.9%; male: 79.5%; female: 60.4% (2003 est.) |
|
|
| |
back to top |
|
Data code: UG Government type: republic Independence: 9 October 1962 (from UK) Legal system: in 1995, the government restored the legal system to one based on English common law and customary law; accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction, with reservations |
|
| back to top | ||
|
Economy-overview:
Uganda has substantial natural resources, including fertile soils, regular
rainfall, and sizable mineral deposits of copper and cobalt. Agriculture is the
most important sector of the economy, employing over 80% of the work force.
Coffee is the major export crop and accounts for the bulk of export revenues.
Since 1986, the government-with the support of foreign countries and
international agencies-has acted to rehabilitate and stabilize the economy by
undertaking currency reform, raising producer prices on export crops,
increasing prices of petroleum products, and improving civil service wages. The
policy changes are especially aimed at dampening inflation and boosting
production and export earnings. In 1990-98, the economy turned in a solid
performance based on continued investment in the rehabilitation of
infrastructure, improved incentives for production and exports, reduced
inflation, gradually improved domestic security, and the return of exiled
Indian-Ugandan entrepreneurs. Continuation of this performance, while possible,
appears difficult because of Ugandan involvement in the war in the Democratic
Republic of the Congo, growing corruption within the government, and slippage
in the government's determination to press reforms.
GDP - real growth rate: 5% (2006 est.) GDP - composition by sector: agriculture: 29.4%; industry: 22.1%; services: 48.5% (2006 est.) Labor force: 13.76 million (2006
est.) Labor force-by occupation: agriculture 86%, industry 4%, services 10% (1980 est.) Industries: sugar, brewing, tobacco, cotton textiles, cement Industrial production growth rate: 5.2% (2006 est.)
|
||
|
Agriculture-products: coffee, tea, cotton, tobacco, cassava (tapioca), potatoes, corn, millet, pulses; beef, goat meat, milk, poultry Exports: $476 million (f.o.b., 1998) Exports-commodities: coffee 54%, gold, fish and fish products, cotton, tea, corn (1997) Exports-partners: Spain 14%, Germany 14%, Netherlands 10%, France 8%, Italy (1997) Imports: $1.4 billion (c.i.f., 1998) Imports-commodities: transportation equipment, petroleum, medical supplies, iron and steel (1996) Imports-partners: Kenya 31%, UK 12%, Japan 6%, India 6%, South Africa 5% (1997) Currency: 1 Ugandan shilling (USh) = 100 cents Exchange rates: Ugandan shillings (USh) per US$1-1,368.4 (December 1998), 1,240.2 (1998), 1,083.0 (1997), 1,046.1 (1996), 968.9 (1995), 979.4 (1994) |
|
|
| |
back to top | ||
|
Telephone
system: fair system but in serious need of expansion and
better maintenance; a cellular system has been introduced as a stopgap but the
communications problems will not be solved without substantial investment in
the conventional telephone infrastructure; e-mail and Internet services are
available Radio broadcast stations: AM 10, FM 0, shortwave 0 Television broadcast stations: 8 (in addition, there is one low-power repeater) (1997) Internet country code: .ug Internet hosts: 1,365 (2006) Internet users: 500,000 (2005) |
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|
Gros PM, Rejmanek M. 1999. Status and habitat preferences of Uganda cheetahs: an attempt to predict carnivore occurrence based on vegetation structure. Biodiversity and Conservation 8, 1561-1583. Marker L., Malouf J. and Malouf A., 1999. Appendix 2: The status of the wild cheetah in its range countries. In: 1999 International Cheetah Studbook. https://www.cia.gov/cia/publications/factbook/geos/ug.html http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Uganda |