|
|  |
| back to top | ||
|
Population. No recent information due to
the long-standing civil war. Estimate
of 500 with a range of 200 - 1000 animals.
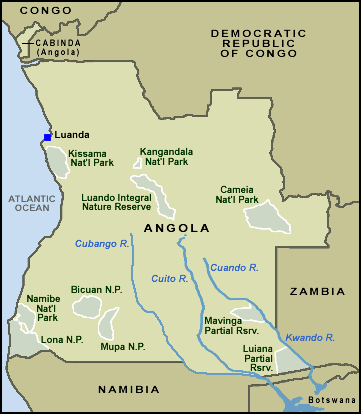
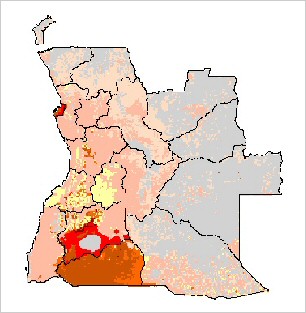
Range was confined to the drier, arid areas in the central and southern
parts of the country. In 1975 cheetah
were reported in the following parks and protected areas: Iona National Park (14,500 Km2), Bicuar
National Park (7,900 Km2), Cameia National Park (14,450km2), Luando National
Park (8,280 km2), Quicama National Park.
The cheetah was declared protected game in 1957, but legislation is
difficult to enforce, and the military community is exempt from these
provisions of the law. In early 2010, cheetahs were confirmed in Iona National Park (see news)
|
|
|
| back to top | |
|
Angola is rebuilding its country after the end of a 27-year civil war in 2002. Fighting between the Popular Movement for the Liberation of Angola (MPLA), led by Jose Eduardo DOS SANTOS, and the National Union for the Total Independence of Angola (UNITA), led by Jonas SAVIMBI, followed independence from Portugal in 1975. Peace seemed imminent in 1992 when Angola held national elections, but UNITA renewed fighting after being beaten by the MPLA at the polls. Up to 1.5 million lives may have been lost - and 4 million people displaced - in the quarter century of fighting. SAVIMBI's death in 2002 ended UNITA's insurgency and strengthened the MPLA's hold on power. While President DOS SANTOS had pledged to hold legislative elections in 2007, he has since announced that legislative elections will be held in 2008, with Presidential elections planned for 2009. A specific election timetable has yet to be established. | |
| back to top | |
|
Area: total: 1,246,700 km2; land: 1,246,700 km2; water: 0 km2 Climate: semiarid in south and along coast to Luanda; north has cool, dry season (May to October) and hot, rainy season (November to April) Terrain: narrow coastal plain rises abruptly to vast interior plateau Natural resources: petroleum, diamonds, iron ore, phosphates, copper, feldspar, gold, bauxite, uranium Land use: arable land: 2.41%; permanent crops: 0.24%; other: 97.35% (2001) Irrigated land: 750 sq km (1998 est.) Natural hazards: locally heavy rainfall causes periodic flooding on the plateau Environment-current issues: the overuse of pastures and subsequent soil erosion attributable to population pressures; desertification; deforestation of tropical rain forest, in response to both international demand for tropical timber and to domestic use as fuel, resulting in loss of biodiversity; soil erosion contributing to water pollution and silting of rivers and dams; inadequate supplies of potable water Environment-international agreements: party to: Biodiversity, Desertification, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution; signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements | |
|
| |
|
|
|
| back to top | ||
|
Population: 12,127,071 (July 2006 est.) Age structure: 0-14 years: 43.4% (male 2,454,209/female 2,407,083); 15-64 years: 53.7% (male 3,059,339/female 2,955,060);65 years and over: 2.8% (male 139,961/female 175,134) (2005 est.) Median age: total: 18.12 years; male: 18.12 years; female: 18.11 years (2005 est.) Population growth rate: 1.9% (2005 est.) Infant mortality rate: total: 191.19 deaths/1,000 live births; male: 203.68 deaths/1,000 live births; female: 178.07 deaths/1,000 live births (2005 est.) Life expectancy at birth: total population: 38.43 years; male: 37.28 years; female: 39.64 years (2005 est.) Total fertility rate: 6.27 children born/woman (2005 est.) HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate: 3.9% (2003 est.) HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS: 240,000 (2003 est.) HIV/AIDS - deaths: 21,000 (2003 est.) |
| |
|
Major infectious diseases: degree of risk: very high; food or waterborne diseases: bacterial and protozoal diarrhea, hepatitis A, typhoid fever; vectorborne diseases: malaria, African trypanosomiasis (sleeping sickness) are high risks in some locations; respiratory disease: meningococcal meningitis; water contact disease: schistosomiasis (2004) | ||
|
Ethnic groups: Ovimbundu 37%, Kimbundu 25%, Bakongo 13%, mestico (mixed European and native African) 2%, European 1%, other 22% Religions: indigenous beliefs 47%, Roman Catholic 38%, Protestant 15% (1998 estimate). Language: Portuguese (official), Bantu and other African languages Ethnic groups: Ovimbundu 37%, Kimbundu 25%, Bakongo 13%, mestico (mixed European and native African) 2%, European 1%, other 22% Religions: indigenous beliefs 47%, Roman Catholic 38%, Protestant 15% (1998 estimate). Language: Portuguese (official), Bantu and other African languages Literacy: definition: age 15 and over can read and write; total population: 66.8%; male: 82.1%; female: 53.8% (2001 est.) |
|
|
| back to top | |
|
Data code: AO Government type: republic, nominally a multiparty democracy with a strong presidential system Independence: 11 November 1975 (from Portugal) Legal system: based on Portuguese civil law system and customary law; recently modified to accommodate political pluralism and increased use of free markets Political pressure groups and leaders: Front for the Liberation of the Enclave of Cabinda or FLEC [N'zita Henriques TIAGO, Antonio Bento BEMBE]; note: FLEC is waging a small-scale, highly factionalized, armed struggle for the independence of Cabinda Province | |
| back to top | |
|
Economy-overview: Angola's high growth rate is driven by its oil sector, but record oil prices and rising petroleum production have occurred without improved performance in other parts of the economy. Oil production and its supporting activities, contribute about 45% to GDP and more than half of exports, and much of the country's infrastructure is still damaged or undeveloped from the 22 year-long civil war. Remnants of the conflict such as widespread land mines still mar the countryside even though an apparently durable peace has been established after the death of rebel leader Jonas SAVIMBI in February 2002. Subsistence agriculture provides the main livelihood for 85% of the population, but much of the country's food must still be imported. In 2005, the government started using a $2 billion line of credit from China to rebuild Angola's public infrastructure, and several large-scale projects are scheduled for completion by 2006. The central bank in 2003 implemented an exchange rate stabilization program using foreign exchange reserves to buy kwanzas out of circulation, a policy that was more sustainable in 2005 because of strong oil export earnings, and has significantly reduced inflation. Consumer inflation declined from 325% in 2000 to about 18% in 2005, but the stabilization policy places pressure on international net liquidity. To fully take advantage of its rich national resources - gold, diamonds, extensive forests, Atlantic fisheries, and large oil deposits - Angola will need to continue reforming government policies and to reduce corruption. The government has made sufficient progress on reforms recommended by the IMF, such as promoting greater transparency in government spending, and continues to be without a formal monitoring agreement with the institution. Increased oil production supported 12% growth in 2004 and 14% growth in 2005. | |
|
GDP - real growth rate: 14.1% (2005 est.) GDP - composition by sector: agriculture: 8%; industry: 67%; services: 25% (2001 est.) Labor force: 6.393 million (2006 est.) Labor force - by occupation: agriculture 85%, industry and services 15% (2003 est.) Unemployment rate: extensive unemployment and underemployment affecting more than half the population (2001 est.) Population below poverty line: 70% (2003 est.) Agriculture-products:
bananas,
sugarcane, coffee, sisal, corn, cotton, manioc (tapioca), tobacco, vegetables,
plantains; livestock; forest products; fish |
|
|
Industries: petroleum; diamonds, iron ore, phosphates, feldspar, bauxite, uranium, and gold; cement; basic metal products; fish processing; food processing; brewing; tobacco products; sugar; textiles Industrial production growth rate: 1% (2000) Exports: $26.8 billion f.o.b. (2005 est.) Exports-commodities: crude oil 90%, diamonds, refined petroleum products, gas, coffee, sisal, fish and fish products, timber, cotton (1998) Exports-partners: US 37.7%, China 35.6%, Taiwan 6.7%, France 6.4% (2004) Imports: $8.165 billion f.o.b. (2005 est.) Imports-commodities: machinery and electrical equipment, vehicles and spare parts; medicines, food, textiles and clothing; substantial military goods Imports-partners: South Korea 28.3%, Portugal 13.1%, US 9.3%, South Africa 7.4%, Brazil 5.6%, Japan 4.8%, France 4.4% (2004) Currency (code): kwanza (AOA) Exchange rates: kwanza per US dollar - 88.6 (2005), 83.541 (2004), 74.606 (2003), 43.53 (2002), 22.058 (2001) |
|
| back to top | |
|
Telephone system: general assessment: telephone service limited mostly to government and business use; HF radiotelephone used extensively for military links; domestic: limited system of wire, microwave radio relay, and tropospheric scatter; international: country code - 244; satellite earth stations - 29; fiber optic submarine cable (SAT-3/WASC) provides connectivity to Europe and Asia (2005) Radio broadcast stations: AM 21, FM 6, shortwave 7 (2000) Television broadcast stations: 6 (2000) Internet country code: .ao Internet hosts: 2,525 (2005) Internet users: 172,000 (2005) | |
| back to top | |
|
Marker L., Malouf J. and Malouf A. 1999. Appendix 2: The status of the wild cheetah in its range countries. In: 1999 International Cheetah Studbook. http://www.cia.gov/cia/publications/factbook/geos/ao.html (last update on 10 January, 2006) http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Angola http://www.eyesonafrica.net/angola-safari.htm http://www.lib.utexas.edu/maps/map_sites/country_sites.html#angola | |